- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-17 Origin: Site

Stud bolts are very important in many industries.
People often make them from carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, or superalloys.
The material chosen depends on how strong the bolt needs to be.
It also depends on how much rust protection is needed.
The place where the stud bolt will be used matters too.
These materials help stud bolts work well in many situations.
Engineers pick the best stud bolt for each job to keep things safe.
Using the right stud bolt can help things last longer and work better.
Carbon steel is used a lot for stud bolts.
It is made mostly of iron with a little carbon.
This steel is strong and not expensive.
People use carbon steel bolts in buildings and machines.
They are good when you need strength but not much rust protection.
Tests show carbon steel bolts are strong and safe.
They can take high heat, but get weaker over 300°C.
New rules help engineers use these bolts safely.
Carbon steel bolts are strong and cheap for many jobs.
Stainless steel bolts do not rust easily.
They have chromium, which makes a shield on the bolt.
This shield stops rust and helps in wet places.
Stainless steel bolts are used in boats, factories, and food plants.
Stainless Steel Grade | Chromium (%) | Nickel (%) | Carbon (%) Max | Molybdenum (%) Max | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Type 304 | 17-19 | 8-12 | 0.08 | N/A | Good against rust; used a lot |
Type 316 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 0.08 | 2.00 | Best for saltwater and chemicals |
Type 410 | 11.5-13.5 | N/A | 0.15 | N/A | Can be made harder; used in roofs |
Type 316 is better than Type 304 for salty water.
Type 316 costs more and is less bendy.
Type 304 is used most for bolts.
Sometimes, stainless bolts stick together, so use special paste.
Alloy steel bolts have extra metals like chromium or nickel.
These metals make the bolts stronger and tougher.
Alloy steel bolts are used in power plants and big machines.
Bolts like ASTM B7 and B8 are very strong.
They have 0.10% to 0.45% carbon and can be super strong.
Tests show alloy bolts hold more weight than others.
Engineers pick these bolts for tough and strong jobs.
Alloy steel bolts are best for hard and heavy work.
Superalloy bolts are made from special metals like nickel.
They stay strong and do not rust, even when very hot.
Superalloys are used in planes, turbines, and oil plants.
Performance Metric | Observation / Result | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
Initial stiffness | Gets lower as it gets hotter | Up to 750°C |
Load-bearing capacity | Changes with heat and bolt fit | 25°C to 750°C |
Failure load (neat-fit joint) | Goes up a bit to 150°C, then drops fast at higher heat | 25°C to 450°C |
Nickel alloys like Alloy 660 and MP159 are very strong.
They do not break or rust at high heat.
Special treatments make them last even longer.
Superalloy bolts are needed where heat and rust are big problems.
Superalloy bolts keep important machines safe in hard places.
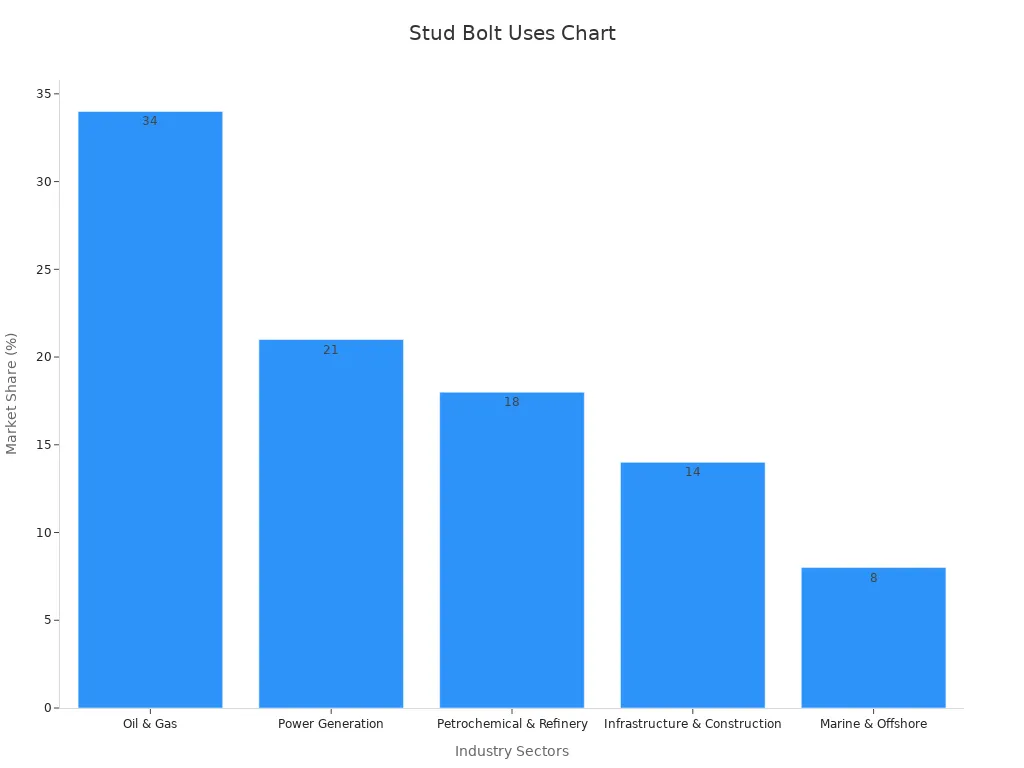
Stud bolts are used in many jobs.
They help hold things together where safety is important.
The table below shows how different jobs use stud bolts.
Industry Sector | Market Share (%) | Key Uses and Notes |
|---|---|---|
Oil & Gas | 34 | Used most; needed for strong and rust-proof bolts. |
Power Generation | 21 | Hold turbines, generators, and other big machines in place. |
Petrochemical & Refinery | 18 | Needed for pipes and tanks in chemical plants. |
Infrastructure & Construction | 14 | Used in bridges, buildings, and roads. |
Marine & Offshore | 8 | Needed for boats and places with lots of water. |
Stud bolts help build bridges, buildings, and roads.
Workers use them to join steel beams and heavy tools.
Rules like ASME B18.2.1 and ASTM set the right size and strength.
If the wrong bolt is used, it can break or rust.
For example, strong steel bolts can crack if it is wet.
Engineers must choose the right bolt for each job.
Note: Broken bolts in bridges show why picking the right bolt is important.
Petrochemical plants need bolts that can take heat and pressure.
These places follow rules from groups like API and NACE.
Stainless steel and special bolts do not rust and keep pipes tight.
Using moly grease helps bolts turn without damage.
Bolts must be tightened just right to stop leaks.
Testing and checks help keep everyone safe.
API and BSEE make rules to protect workers and machines.
Engineers test bolts to make sure they are tight enough.
Cars and planes use stud bolts in engines and frames.
These bolts face fast speeds and lots of force.
Labs test bolts for strength and hardness.
Certifications like ISO/IEC 17025 and Nadcap show bolts are safe.
Planes use only the best bolts, like superalloys.
This keeps people safe when they travel.
Factories and power plants use stud bolts in machines.
Bolts must hold heavy parts and stop shaking.
Stainless and alloy steel bolts last longer and do not rust.
In power plants, bolts hold turbines and boilers.
In wind and solar power, bolts keep towers and panels safe.
The right bolt keeps machines working and saves time.
Tip: Picking the right bolt helps stop breaks and saves money.
Engineers check the place before picking a stud bolt.
Things like heat, cold, wetness, and chemicals matter a lot.
Cold can make some bolts stronger.
Heat or salty water can make bolts rust or get weak.
Bolts lose strength faster in tough places like the ocean.
Stainless and coated bolts can get loose in these spots.
Special bolts like GFRP may break after a long time.
Tools like Tally and e-tool LCD help pick better bolts.
These tools show which bolts last longer and hurt the earth less.
They also help compare bolts for better use and care.
Tip: Always check where bolts will go to stop early breaks.
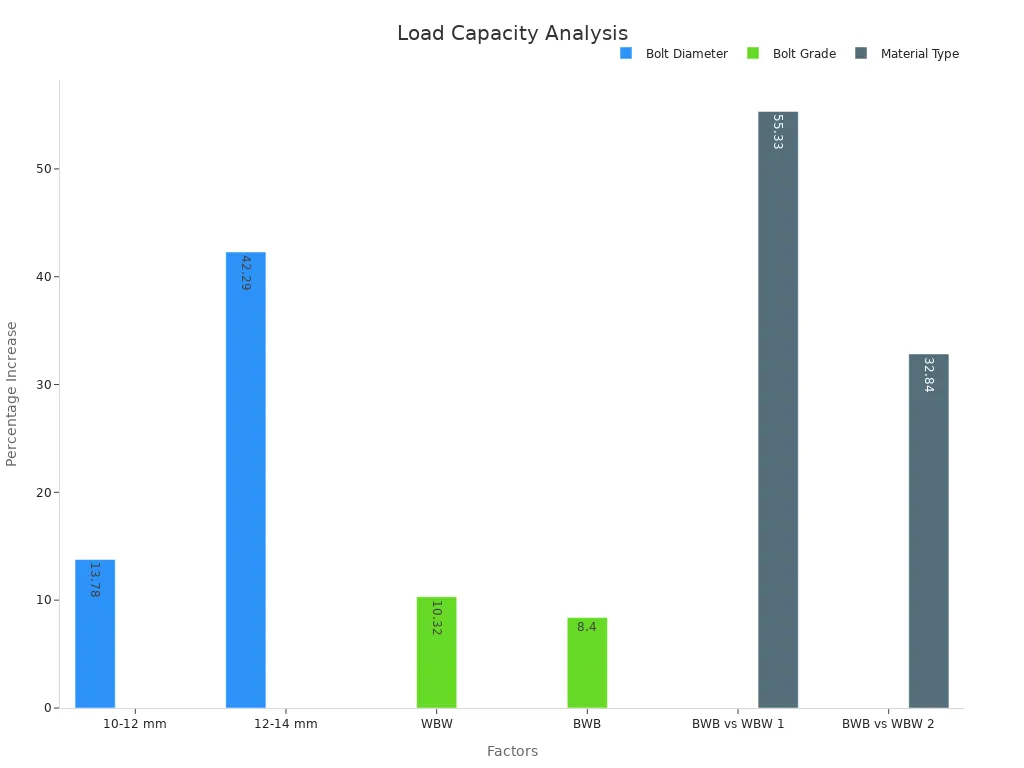
How much weight a bolt holds is very important.
Engineers test bolts for how strong and hard they are.
These tests show when a bolt will bend or snap.
Big bolts and higher grades can hold more weight.
Tests and computer models help guess how bolts will do.
The chart below shows how size and type change strength.
Pick a bolt that is strong enough for the job.
Heavy machines need very strong bolts.
Good bolts match the job’s weight for safe work.
Rules help bolts and nuts fit and work together.
Groups like ASTM, ISO, ANSI, and ASME make these rules.
They say what size, shape, and metal bolts should be.
For example, ASTM A193 bolts fit ASTM A194 nuts.
Rules also tell how tight bolts should be and how to put them in.
Certificates show bolts and nuts are good quality.
Install bolts with clean threads and the right tools.
This keeps things safe and tight.
ASTM, ISO, DIN, and SAE all make bolt rules.
Bolts and nuts must match in size and metal.
Always use the right steps to put bolts in.
Note: The right bolts and nuts stop breaks and keep things safe.
Coatings help keep stud bolts safe from rust and harm.
Many jobs use coatings to stop rust, especially in wet or salty places.
A coating makes a shield that blocks water, salt, and chemicals.
This shield helps the stud bolt last longer and work better.
Tests show epoxy and rubber coatings protect well in hard places.
Epoxy with titanium dioxide makes a thick, strong layer.
This layer sticks tight and keeps out bad stuff.
Galvanized coatings use zinc to guard the steel inside.
The zinc takes the damage first to stop rust.
But near the sea, even zinc and black coatings can fail fast.
This can hurt the threads and make the stud bolt break.
Stainless steel bolts fight rust better, but salty air can still hurt them.
Tip: Coatings must cover the whole stud bolt with no gaps.
Cracks or holes let water in and cause hidden problems.
Engineers use different coatings to help stud bolts last longer.
Each coating gives a different level of rust protection and strength.
Hot-dip galvanizing: Puts a thick zinc layer on the stud bolt.
It gives fair protection and lasts about 250 hours in salt spray.
Thermo-diffusion (TD) coating: Bonds zinc and steel very well.
TD coatings can last up to 1000 hours before rust shows.
Cataphoretic coating: This thin layer gives fair protection.
It lasts 480 to 1000 hours in salt spray but can wear off faster.
Zinc lamella: Uses tiny zinc flakes mixed with glue.
Small flakes and about 30–35% glue make it work best.
Epoxy and chlorinated rubber: Make a tight, strong layer.
They block water and chemicals in wet or chemical places.
Coating Type | Salt Spray Resistance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Thermo-diffusion (TD) | ~1000 hours | Best at stopping rust |
Hot-dip galvanizing | ~250 hours | Zinc takes damage first |
Cataphoretic coating | 480–1000 hours | Less friction, wears down faster |
Zinc lamella | Varies | Works best with small flakes/glue |
Epoxy/Chlorinated Rubber | High | Strong shield, blocks chemicals |
Pick the right coating for where the stud bolt will go.
Some coatings, like zinc, protect by wearing away first.
Others, like epoxy, act as a strong wall.
Engineers must choose the best coating for each job.
Picking the right stud bolt material keeps things safe.
Engineers choose bolts and nuts that fit the job.
They add coatings to protect bolts from rust.
It is important that bolts and nuts fit together well.
Using the right rules makes machines and buildings strong.
Experts can help pick the safest bolts for hard jobs.
Fully threaded stud bolts have threads along the entire length. Double-end stud bolts have threads only at both ends. Each type fits different uses. Engineers pick the right one based on the design and structure of a stud bolt.
Tap-end stud bolts work best in heavy machinery and engines. One end has longer threads for nuts. The other end has shorter threads for screwing into a tapped hole. This design helps hold parts tightly.
Weld stud bolts attach directly to metal surfaces by welding. Workers use them in construction and shipbuilding. This method creates a strong bond. Weld stud bolts help connect steel plates and frames.
The design and structure of a stud bolt decide how much weight it can hold. Different shapes and threads fit different jobs. Engineers study these features to make sure the bolt works safely.
Engineers often use fully threaded stud bolts in high-pressure pipes and flanges. The threads give a strong grip. This helps prevent leaks and keeps the system safe.